Goal
Dive into the vibrant world of CIFAR image datasets through a meticulously designed neural network model. Utilizing the power of PyTorch, this project underscores the nuances of handling multi-class image classifications. The network, calibrated and assessed on the CIFAR dataset, showcases the synergy between convolutional strategies and advanced optimization techniques, transforming raw pixel values into discernible object classifications.
Import Packages
import os
if ('google' in str(get_ipython())):
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('ME')
#predir='/content/ME/My Drive/'
predir='ME/My Drive/'
else:
predir = os.path.join('Users','amit','Google Drive')
if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(predir,'My Drive')):
predir=os.path.join(predir,'My Drive')
import torch
import numpy as np
# Torch functions
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
# Utility to track progress of a routine.
#from tqdm import tqdm
from tqdm.notebook import trange, tqdm
# Folder with course data
datadir=predir
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
Drive already mounted at ME; to attempt to forcibly remount, call drive.mount("ME", force_remount=True).
Get cifar10 data and split into training, validation and testing.
import h5py
def get_cifar():
with h5py.File(datadir+'cifar10_train.hdf5', "r") as f:
tr=f[('data')][:].transpose(0,3,1,2)
tr_lb=f[('labels')][:]
train_data=np.float32(tr[0:45000])/255.
train_labels=tr_lb[0:45000]
val_data=np.float32(tr[45000:])/255.
val_labels=tr_lb[45000:]
with h5py.File(datadir+'cifar10_test.hdf5', "r") as f:
test_data=f[('data')][:].transpose(0,3,1,2)
test_data=np.float32(test_data)/255.
test_labels=f[('labels')][:]
return (train_data, train_labels), (val_data, val_labels), (test_data, test_labels)
Get the data
def get_data(data_set):
if (data_set=="mnist"):
return(get_mnist())
elif (data_set=="cifar"):
return(get_cifar())
# An object containing the relevant parameters for running the experiment.
class par(object):
def __init__(self):
self.batch_size=1000
self.step_size=.001
self.num_epochs=20
self.numtrain=10000
self.minimizer="Adam"
self.data_set="cifar"
self.model_name="model"
self.dropout=0.
self.dim=32
self.pool_size=2
self.kernel_size=5
self.mid_layer=256
self.use_gpu=False
pars=par()
train,val,test=get_data(data_set=pars.data_set)
num_images = 10
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, num_images, figsize=(15, 3))
for i in range(num_images):
img = train[0][i].transpose(1, 2, 0)
axes[i].imshow(img)
axes[i].axis('off')
axes[i].set_title(f'Label: {train[1][i]}')
plt.show()

class CIFAR_Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,pars):
super(CIFAR_Net, self).__init__()
ks = pars.kernel_size
ps = np.int32(pars.pool_size)
self.mid_layer = pars.mid_layer
# Two successive convolutional layers.
# Two pooling layers that come after convolutional layers.
# Two dropout layers.
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=ks[0], padding=ks[0] // 2)
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=[ps], stride=2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=ks[1], padding=ks[1] // 2)
self.drop2 = nn.Dropout2d(pars.dropout)
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.drop_final = nn.Dropout(pars.dropout)
# Run the network one time on one dummy data point of the same
# dimension as the input images to get dimensions of fully connected
# layer that comes after second convolutional layers
self.first=True
if self.first:
self.forward(torch.zeros((1,)+pars.inp_dim))
# Setup the optimizer type and send it the parameters of the model
if pars.minimizer == 'Adam':
self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr = pars.step_size)
else:
self.optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(self.parameters(), lr = pars.step_size)
self.criterion=nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
def forward(self, x):
# Apply relu to a pooled conv1 layer.
x = F.relu(self.pool1(self.conv1(x)))
if self.first:
print('conv1',x.shape)
# Apply relu to a pooled conv2 layer with a drop layer inbetween.
x = self.drop2(F.relu(self.pool2(self.conv2(x))))
if self.first:
print('conv2',x.shape)
if self.first:
self.first=False
self.inp=x.shape[1]*x.shape[2]*x.shape[3]
# Compute dimension of output of x and setup a fully connected layer with that input dim
# pars.mid_layer output dim. Then setup final 10 node output layer.
print('input dimension to fc1',self.inp)
if self.mid_layer is not None:
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(self.inp, self.mid_layer)
self.fc_final = nn.Linear(self.mid_layer, 10)
else:
self.fc1=nn.Identity()
self.fc_final = nn.Linear(self.inp, 10)
# Print out all network parameter shapes and compute total:
tot_pars=0
for k,p in self.named_parameters():
tot_pars+=p.numel()
print(k,p.shape)
# Calculate and print the number of parameters
print('tot_pars',tot_pars)
x = x.reshape(-1, self.inp)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.drop_final(x)
x = self.fc_final(x)
return x
# Run the network on the data, compute the loss, compute the predictions and compute classification rate/
def get_acc_and_loss(self, data, targ):
output = self.forward(data)
loss = self.criterion(output, targ)
pred = torch.max(output,1)[1]
correct = torch.eq(pred,targ).sum()
return loss,correct
# Compute classification and loss and then do a gradient step on the loss.
def run_grad(self,data,targ):
loss, correct=self.get_acc_and_loss(data,targ)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
return loss, correct
# use GPU when possible
pars.device = device
pars.kernel_size=[5,5]
train,val,test=get_data(data_set=pars.data_set)
pars.inp_dim=train[0][0].shape
# Initialize the network
net = CIFAR_Net(pars).to(pars.device)
# Post it to the gpu if its there.
net.to(pars.device)
conv1 torch.Size([1, 32, 16, 16])
conv2 torch.Size([1, 64, 8, 8])
input dimension to fc1 4096
conv1.weight torch.Size([32, 3, 5, 5])
conv1.bias torch.Size([32])
conv2.weight torch.Size([64, 32, 5, 5])
conv2.bias torch.Size([64])
fc1.weight torch.Size([256, 4096])
fc1.bias torch.Size([256])
fc_final.weight torch.Size([10, 256])
fc_final.bias torch.Size([10])
tot_pars 1105098
CIFAR_Net(
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(pool1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=[2], stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv2): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(drop2): Dropout2d(p=0.0, inplace=False)
(pool2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(drop_final): Dropout(p=0.0, inplace=False)
(fc1): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=256, bias=True)
(fc_final): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=10, bias=True)
(criterion): CrossEntropyLoss()
)
# use GPU when possible
pars.device = device
pars.kernel_size=[5,5]
train,val,test=get_data(data_set=pars.data_set)
pars.inp_dim=train[0][0].shape
# Initialize the network
net = CIFAR_Net(pars).to(pars.device)
# Post it to the gpu if its there.
net.to(pars.device)
train=(train[0][0:pars.numtrain],train[1][0:pars.numtrain])
# Initialize lists to store the training and validation error rates.
train_error_rates = []
test_error_rates = []
for i in range(pars.num_epochs):
# Run one epoch of training
train_error_rates.append(run_epoch(net, i, train, pars, num=pars.numtrain, ttype="train"))
# Test on validation set.
test_error_rates.append(net_test(net, val, pars))
original_train_error_rates = train_error_rates
original_test_error_rates = test_error_rates
# Save the model to a file
if not os.path.isdir(os.path.join(predir,'part2b')):
os.mkdir(os.path.join(predir,'part2b'))
torch.save(net.state_dict(), os.path.join(predir,'part2b',pars.model_name))
conv1 torch.Size([1, 32, 16, 16])
conv2 torch.Size([1, 64, 8, 8])
input dimension to fc1 4096
conv1.weight torch.Size([32, 3, 5, 5])
conv1.bias torch.Size([32])
conv2.weight torch.Size([64, 32, 5, 5])
conv2.bias torch.Size([64])
fc1.weight torch.Size([256, 4096])
fc1.bias torch.Size([256])
fc_final.weight torch.Size([10, 256])
fc_final.bias torch.Size([10])
tot_pars 1105098
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 0: Avg. loss: 0.0022, Accuracy: 1963/10000 (19.63%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0021, Accuracy: 1261/5000 (25.22%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 1: Avg. loss: 0.0020, Accuracy: 2825/10000 (28.25%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0019, Accuracy: 1569/5000 (31.38%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 2: Avg. loss: 0.0018, Accuracy: 3537/10000 (35.37%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0018, Accuracy: 1808/5000 (36.16%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 3: Avg. loss: 0.0017, Accuracy: 4019/10000 (40.19%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0017, Accuracy: 2048/5000 (40.96%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 4: Avg. loss: 0.0016, Accuracy: 4382/10000 (43.82%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0016, Accuracy: 2055/5000 (41.10%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 5: Avg. loss: 0.0015, Accuracy: 4499/10000 (44.99%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0016, Accuracy: 2183/5000 (43.66%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 6: Avg. loss: 0.0015, Accuracy: 4675/10000 (46.75%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0016, Accuracy: 2210/5000 (44.20%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 7: Avg. loss: 0.0015, Accuracy: 4778/10000 (47.78%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0015, Accuracy: 2277/5000 (45.54%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 8: Avg. loss: 0.0014, Accuracy: 4963/10000 (49.63%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0014, Accuracy: 2364/5000 (47.28%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 9: Avg. loss: 0.0014, Accuracy: 5038/10000 (50.38%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0014, Accuracy: 2485/5000 (49.70%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 10: Avg. loss: 0.0013, Accuracy: 5271/10000 (52.71%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0014, Accuracy: 2526/5000 (50.52%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 11: Avg. loss: 0.0013, Accuracy: 5374/10000 (53.74%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0014, Accuracy: 2618/5000 (52.36%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 12: Avg. loss: 0.0013, Accuracy: 5472/10000 (54.72%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0013, Accuracy: 2603/5000 (52.06%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 13: Avg. loss: 0.0012, Accuracy: 5609/10000 (56.09%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0013, Accuracy: 2642/5000 (52.84%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 14: Avg. loss: 0.0012, Accuracy: 5698/10000 (56.98%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0013, Accuracy: 2734/5000 (54.68%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 15: Avg. loss: 0.0012, Accuracy: 5793/10000 (57.93%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0013, Accuracy: 2750/5000 (55.00%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 16: Avg. loss: 0.0011, Accuracy: 5879/10000 (58.79%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0013, Accuracy: 2774/5000 (55.48%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 17: Avg. loss: 0.0012, Accuracy: 5931/10000 (59.31%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0013, Accuracy: 2702/5000 (54.04%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 18: Avg. loss: 0.0011, Accuracy: 6059/10000 (60.59%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0012, Accuracy: 2799/5000 (55.98%)
0%| | 0/10 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Training set epoch 19: Avg. loss: 0.0011, Accuracy: 6213/10000 (62.13%)
Validation set: Avg. loss: 0.0012, Accuracy: 2818/5000 (56.36%)
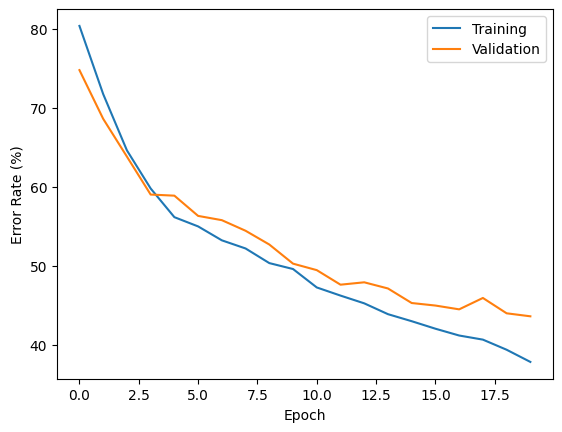
Plot training and validation error against epoch number.
plt.plot(range(pars.num_epochs), train_error_rates, label="Training")
plt.plot(range(pars.num_epochs), test_error_rates, label="Validation")
plt.xlabel("Epoch")
plt.ylabel("Error Rate (%)")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Plot the first layer filters.
filters = net.conv1.weight.detach().cpu().numpy()
fig, axes = plt.subplots(4, 8, figsize=(10, 5))
for i, ax in enumerate(axes.flatten()):
img = filters[i, 0, :, :]
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axis("off")
plt.show()
from skimage.color import rgb2hsv, hsv2rgb
def modify_saturation(data, min_factor=0.75, max_factor=1.25):
images, labels = data
modified_images = []
for img in images:
img_np = img / 255
# Convert to the expected shape (32, 32, 3)
img_np = np.transpose(img_np, (1, 2, 0))
# Convert to HSV
img_hsv = rgb2hsv(img_np)
# Modify saturation
factor = np.random.uniform(min_factor, max_factor) # Moved inside the for loop
img_hsv[:, :, 1] = np.clip(img_hsv[:, :, 1] * factor, 0, 1)
# Convert back to RGB
img_modified = hsv2rgb(img_hsv)
# Convert back to the original shape (3, 32, 32)
img_modified = np.transpose(img_modified, (2, 0, 1))
modified_images.append(img_modified)
modified_images_np = np.array(modified_images) * 255
return (modified_images_np, labels)
Show some of the resulting images.
num_examples = 10
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, num_examples, figsize=(10, 5))
val_sat_dat, val_sat_labels = modify_saturation(val)
for i in range(num_examples):
axes[0, i].imshow(np.transpose(val[0][i], (1, 2, 0)))
if i == 0:
axes[0, i].set_title('Original')
axes[0, i].axis('off')
axes[1, i].imshow(np.transpose(val_sat_dat[i], (1, 2, 0)))
if i == 0:
axes[1, i].set_title('After Saturation')
axes[1, i].axis('off')
plt.show()
